Input Configuration
Introduction
This page describes the contents of the Input tab.
Four tabs
- RC Input to configure the controls,
- Flight Mode Switch Settings to configure how the different flight modes can be selected,
- Failsafe settings to configure the default controls values while failsafe is triggered,
- Arming Settings to configure the input required to arm the model.
RC Input Tab
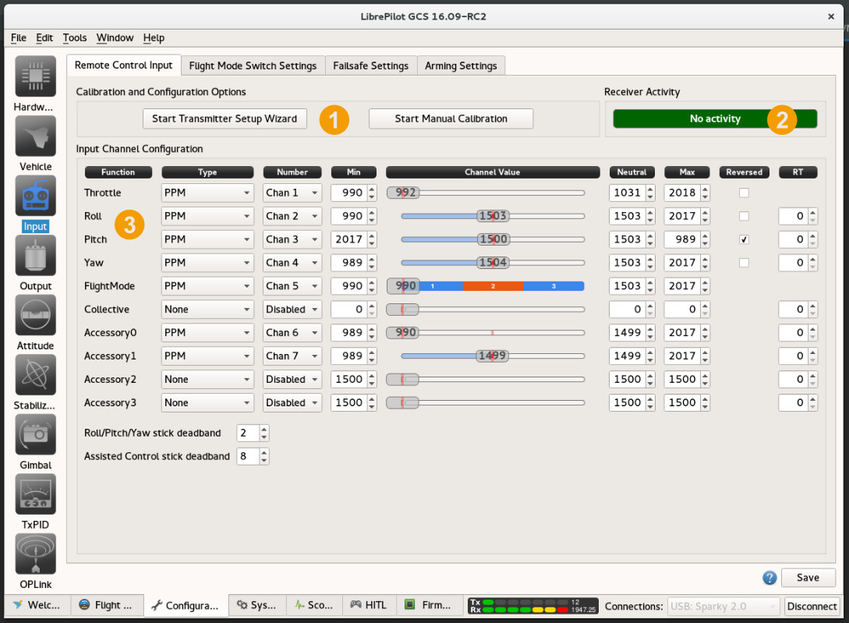
Remote Control Input
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Calibration and Configuration optionsThe two buttons at the top of the page start the Transmitter Setup Wizard, and the Manual Calibration process for the inputs. |
| 2 | Receiver ActivityTells the user about input activity, useful to find the channel assigned to one stick movement or a channel with gitter. |
| 3 | Input Channel ConfigurationThis table links the function with the RC input type and channel, and also allows configuration of signal range. |
Mixed input types
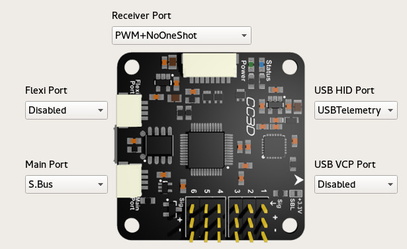
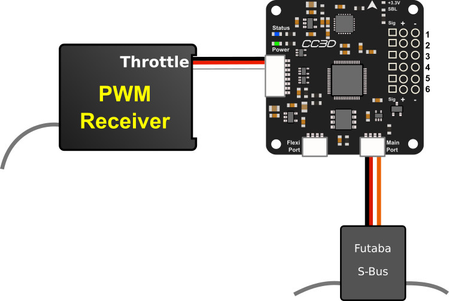
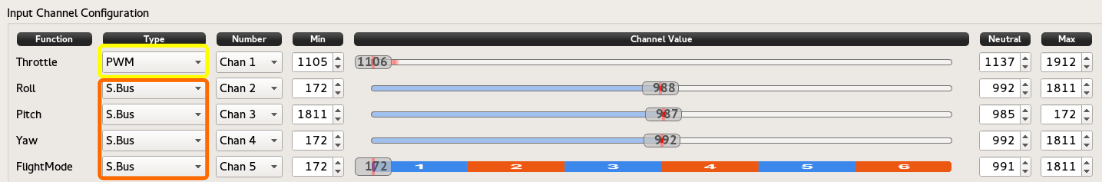
Mixed input types can be used, like one channel using PWM and others using S.Bus.
This means the hardware tab has this input types configured previously.
Flight Mode Switch Settings
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
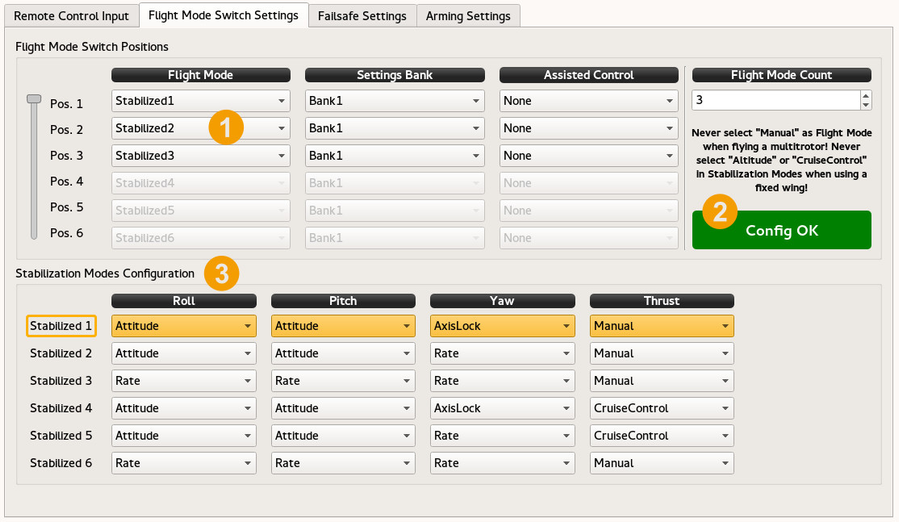
| 1 | Flight Mode Switch PositionsUp to six different flight modes can be configured, provided the transmitter has the capability. The flight modes available depend on the flight controller. |
| 2 | Tells the user if there is something wrong in configuration, can be a not supported FlightMode or incompatible Thrust mode in primary stabilization mode. Heed the warnings about flight mode incompatibility for different airframes!. |
| 3 | Stabilization Modes ConfigurationEach of the six primary Stabilization modes can be configured to utilize appropriate functions based on desired performance.
|
Failsafe Settings
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
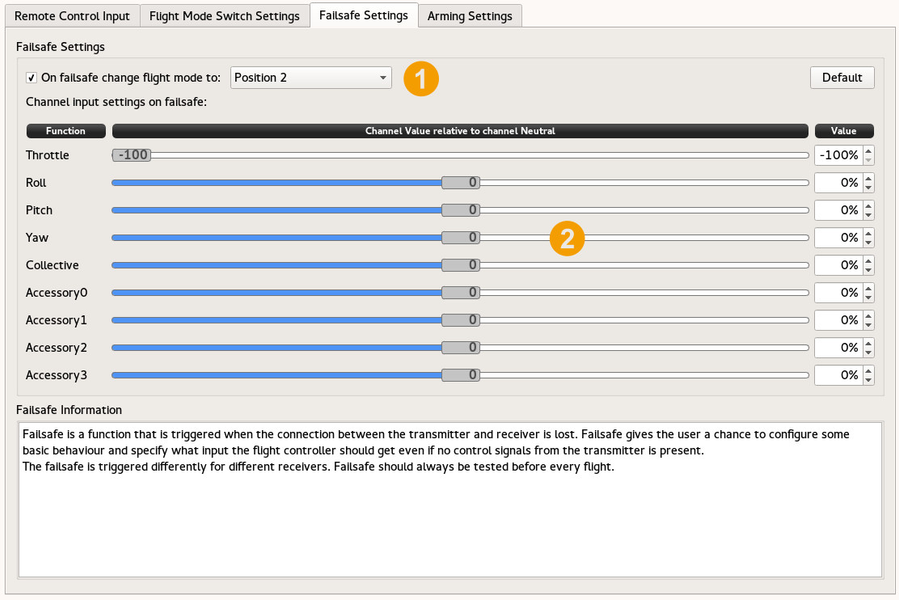
| 1 | Flight ModeRefers to the flightmode position to use while the failsafe is triggered. |
| 2 | Failsafe valuesFailsafe values can be set here, in percent. Positive value if not recommended for Throttle and can give a flyaway instead of a safe "landing". |
There are 2 different Failsafe types: one in the RC receiver and the other in the Flight Controller (this Tab).
Flight Controller Failsafe:
|
RC Failsafe
|
Arming Settings
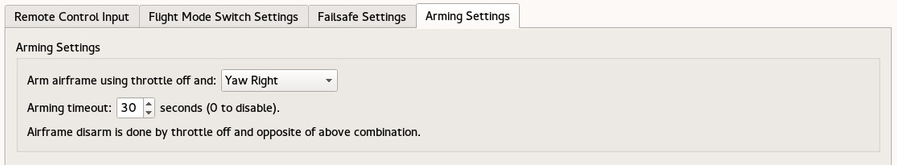
The position of the sticks or Accessory (switch) used for arming the quad are configured here, together with the time out to disable. The airframe is also disarmed manually by the opposite combination of stick positions.
Timeout can be set to zero for Fixed Wing frame, this allow minimal Throttle / gliding phase without disarming board.
About Always armed
Avoid the "Always armed" mode for safe reasons : Try to fix alarms instead, looking at System Health panel.